这篇文章主要介绍了Python中的元组与逻辑运算符的用法,是Python入门学习中的基础知识,需要的朋友可以参考下
Python元组
元组是另一个数据类型,类似于List(列表)。
元组用"()"标识。内部元素用逗号隔开。但是元素不能二次赋值,相当于只读列表。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- tuple = ( 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 ) tinytuple = (123, 'john') print tuple # 输出完整元组 print tuple[0] # 输出元组的第一个元素 print tuple[1:3] # 输出第二个至第三个的元素 print tuple[2:] # 输出从第三个开始至列表末尾的所有元素 print tinytuple * 2 # 输出元组两次 print tuple + tinytuple # 打印组合的元组
以上实例输出结果:
('abcd', 786, 2.23, 'john', 70.2)
abcd
(786, 2.23)
(2.23, 'john', 70.2)
(123, 'john', 123, 'john')
('abcd', 786, 2.23, 'john', 70.2, 123, 'john')
以下是元组无效的,因为元组是不允许更新的。而列表是允许更新的:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- tuple = ( 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 ) list = [ 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'john', 70.2 ] tuple[2] = 1000 # 元组中是非法应用 list[2] = 1000 # 列表中是合法应用
Python逻辑运算符
Python语言支持逻辑运算符,以下假设变量a为10,变量b为20:
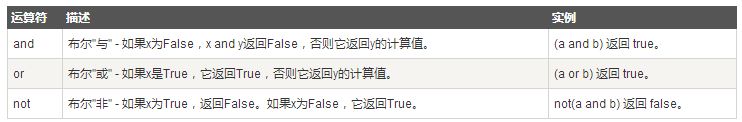
以下实例演示了Python所有逻辑运算符的操作:
#!/usr/bin/python a = 10 b = 20 c = 0 if ( a and b ): print "Line 1 - a and b are true" else: print "Line 1 - Either a is not true or b is not true" if ( a or b ): print "Line 2 - Either a is true or b is true or both are true" else: print "Line 2 - Neither a is true nor b is true" a = 0 if ( a and b ): print "Line 3 - a and b are true" else: print "Line 3 - Either a is not true or b is not true" if ( a or b ): print "Line 4 - Either a is true or b is true or both are true" else: print "Line 4 - Neither a is true nor b is true" if not( a and b ): print "Line 5 - Either a is not true or b is not true or both are not true" else: print "Line 5 - a and b are true"
以上实例输出结果:
Line 1 - a and b are true Line 2 - Either a is true or b is true or both are true Line 3 - Either a is not true or b is not true Line 4 - Either a is true or b is true or both are true Line 5 - Either a is not true or b is not true or both are not true
版权声明:
本站所有资源均为站长或网友整理自互联网或站长购买自互联网,站长无法分辨资源版权出自何处,所以不承担任何版权以及其他问题带来的法律责任,如有侵权或者其他问题请联系站长删除!站长QQ754403226 谢谢。
- 上一篇: 如何准确判断请求是搜索引擎爬虫(蜘蛛)发出的请求
- 下一篇: Python中的字典与成员运算符初步探究







